The types of worms that infect a person's internal organs are called helminths. According to statistics, today about 30% of the total population is susceptible to helminthic invasion. Worms that poison the body can infect any part of the body. This is dangerous not only for diseases that can be caused by helminths. Their presence in the body can be fatal.
To date, helminthiasis can be completely cured not only by drugs but also by folk remedies. Each species has its own methods of treatment. It is therefore worth knowing and understanding what types of worms are, as well as the symptoms of a parasitic infection, in order to take timely action.
Classification of helminthiasis
Parasitic worms are divided into two major groups: intestinal and tissue.
The first species lives directly in the intestines. This group includes:
- roundworms and earthworms;
- ankylosis and lamblia;
- whips and dwarf ribbons;
- beef tapeworm and broad tapeworm;
- pork tapeworm.
Tissue worms can inhabit any organ of the human body and parasitize for many years. These include:
- cysticercus and trematodes;
- Trichinella and liver fluke;
- echinococcus and alveococcus.
Roundworm
They are the most common and demanding worms that live in the small intestine of an adult or child. Infection with this type of helminth is called ascariasis.
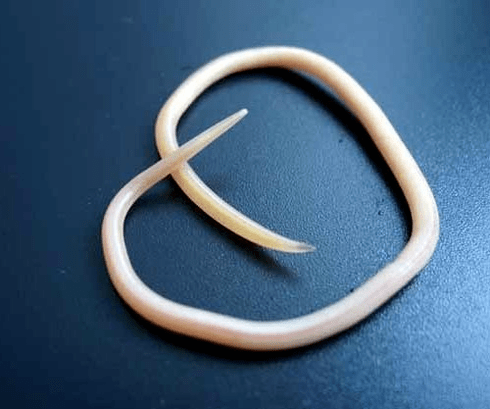
In the first days of the invasion, the person begins to feel weakness, nervousness, fever, shortness of breath, cough and chest pain. Such symptoms are justified by the fact that helminths initially affect the respiratory system.
Infection can occur by drinking raw water from untested sources, poorly processed fresh fruits and vegetables. In summer, the risk of ascariasis is increased.
Pinworms
Small helminths that settle in the intestines cause a disease called enterobiasis. Worms lay eggs in the anal area. The laid eggs turn into larvae and can re-enter the body only through the oral cavity.

Re-infection occurs due to the contact of the dirty hands of a person suffering from enterobiasis with the food he eats. Symptoms of infection may include itching around the anus and increased irritability.
Bitan! The disease is carried by humans.
Hookworm
Infection with rod infections occurs through damaged skin in contact with the ground, where the larvae of these types of worms live.
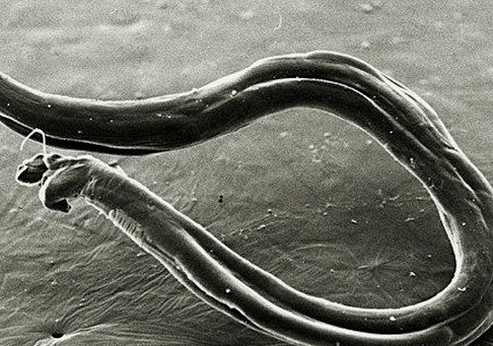
Hookworms, before they enter the intestines, follow the same path as roundworms.
Symptoms include cough, lower abdominal pain, nausea, and stool disorders. This type of helminthiasis can cause anemia.
Garden
Giardiasis progresses in people who have a habit of biting their nails and other objects (pencils, pencils). Infection can also occur in the case of drinking poor quality water, unwashed products, contact with dirty laundry, where there may be larvae, and the carrier of the disease.
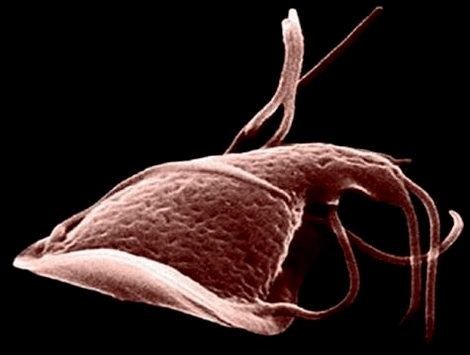
Symptoms of infection may include loose stools and lower abdominal pain.
Vlasoglava
Trichocephaly occurs during infection with beetle larvae. They go inside with unprocessed fruits and vegetables. Dirty hands and water are also vectors.
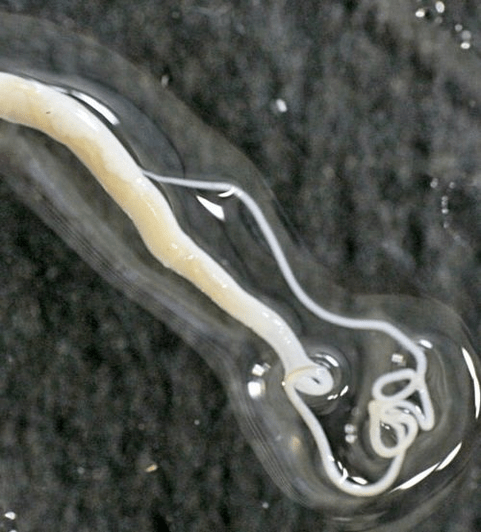
The invasion is accompanied by acute abdominal pain, diarrhea, and decreased appetite. The signs of infection are often similar to those of appendicitis.
Dwarf tapeworm
Worm infection does not only occur with dirty hands and unwashed food, but insects can also be their vector.
Dwarf tapeworm affects the intestines and liver, causing inflammation and poisoning.
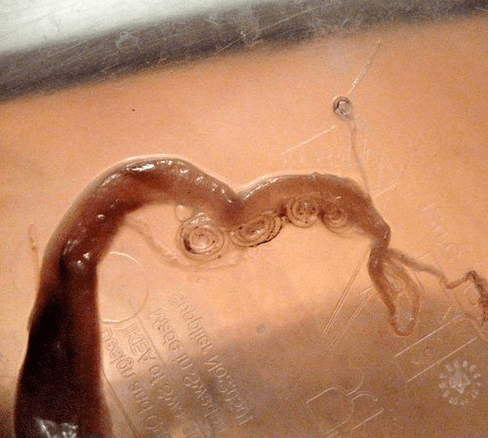
Hymenolepiasis can be accompanied by the appearance of dysbiosis, weakened appetite, increased thirst, increased fatigue and nervousness.
Beef tapeworm
One of the most dangerous types of worms that parasitizes on the colon.

The adult worm reaches several meters in length. An individual takes away all the nutrients from the human body and creates a serious intoxication.
Symptoms of invasion are:
- diarrhea and abdominal pain;
- vomiting and nausea;
- restless sleep;
- dizziness and fainting.
The risk of teniarinhosis occurs when insufficiently processed beef contaminated with tapeworm larvae is eaten.
Wide ribbon
The cause of diphyllobotriasis is the consumption of poorly processed fish products and caviar.
The worm that causes the disease is one of the largest and can reach ten meters.
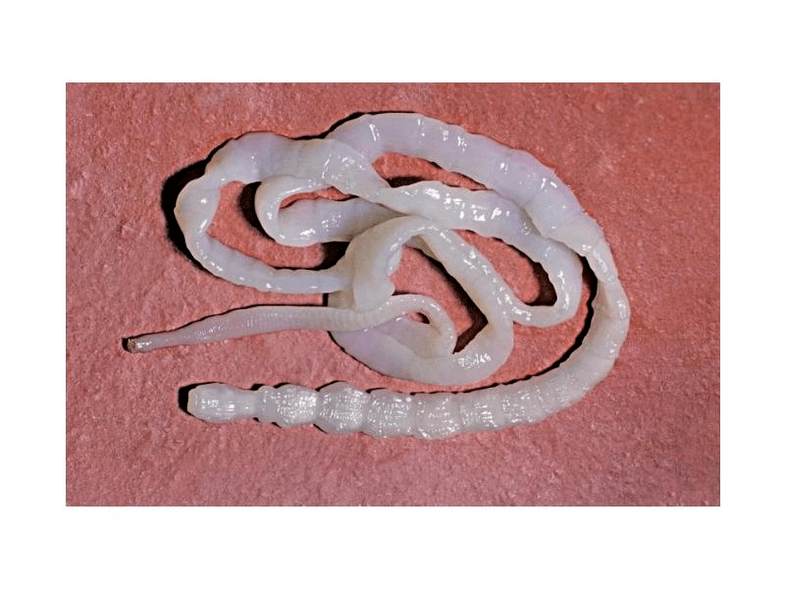

Symptoms of infection include severe lower abdominal pain and anemia.
Pork tapeworm
Infection with this type of helminth is extremely dangerous for humans. If you eat pork that is not cooked enough, Finns can enter the body and become adults.
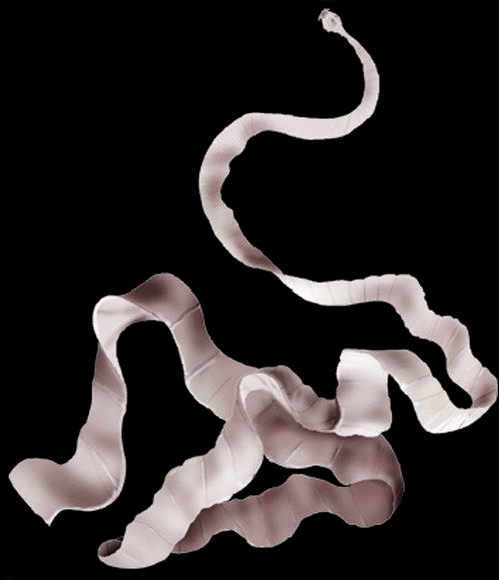
The so-called segments are periodically separated from the body of the porcine tapeworm, which are able to leave the body by themselves through the anus or with feces, entering the environment. The signs of teniasis are similar to those of bovine tapeworm infection.
Cysticers
It is a type of tissue worm that is a product of the pig tapeworm segment. Segments containing tapeworm eggs enter the external environment and can re-enter the body through external environmental objects and cause the development of cysticercosis.

Parasites inhabit muscles, the myocardium, and even the brain.
Bitan! They act on the squeezing of organs and cause inflammation.
Hepatic fluke
Opisthorchiasis occurs as a result of ingestion of liver fluke larvae along with infected fish into the human body.
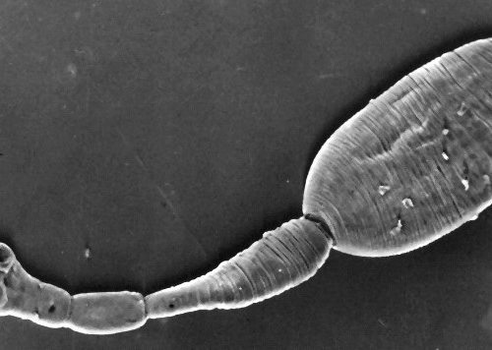
Signs of the presence of opisthorchiasis:
- nausea;
- diarrhea;
- pain all over the body;
- occurrence of allergies.
More serious symptoms are chronic. This type of parasite is dangerous for the development of liver cancer.
Echinococcus
The worm settles in the body, most commonly in the liver or lungs. Echinococcus can cause cysts to form in the affected organ and tumors to appear. Infection can be fatal.
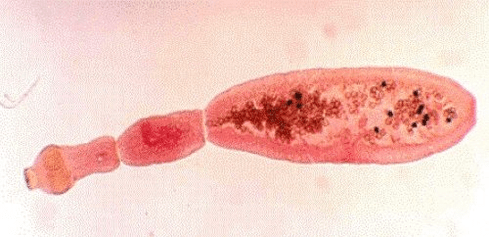
The larvae are transmitted to humans by contact with sick animals.
Trichinella
Trichinosis primarily affects people who eat poorly processed wildlife meat. Pigs can also be carriers of Trichinella.
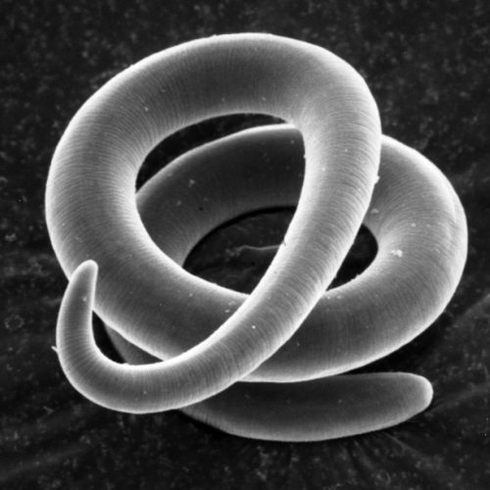
The habitats of adults in the human body are various types of muscles (respiratory, facial, etc. ).
Nausea and loose stools occur at an early stage. The next symptoms of the invasion are fever, edema, skin rash, muscle aches. Infection with this type of parasite without timely treatment can be fatal.
Ways of infecting people with helminths
- Biohelminthiasis (infection of animals).
- Infectious helminthiasis (transmitted from person to person).
- Geohelminthiasis (diseases caused by parasites that spend one of their life cycles in the country).
Factors affecting the manifestations of helminthiasis
The way the parasite enters the body;
- Degree of helminth adaptation to the human body;
- Population density (number) of parasitic individuals;
- Worm habitat (tissue parasites live in the thickness of soft tissues, and luminal in the cavities of hollow organs). Some helminths have different luminal and tissue forms at different stages. Larvae and stages of worm development, as a rule, cause more pronounced pathological changes.
In the absence of re-infection, the number of adult parasites in the human body does not increase. This characteristic significantly distinguishes helminthic invasions from diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi and protozoa.
Worms in humans: symptoms
Helminthiasis is a disease characterized by 2 stages of the course (acute, from two weeks to two months) and chronic (from several months to several years).
Symptoms of the acute phase of helminthiasis
The first signs of the disease may appear at different times (usually after 2-3 weeks, in ascariasis - after 2-3 days, and in filariasis, the incubation period can last 6-18 months).
In the acute phase of parasitic invasion, the most characteristic symptom is an allergic reaction (antibodies are formed to the antigens of the larvae of migrating parasites). Often, people infected with worms develop itchy rashes on the skin, prone to recurrent flow, enlarged regional lymph nodes, generalized or local edema, muscle and joint pain may occur. Also, migrating parasite larvae can cause chest pain, cough, choking attacks, stool disorders, nausea, and vomiting.
Signs of chronic helminthiasis
The symptoms of the chronic phase directly depend on which organ is "inhabited" by parasites, and also their size and number play an important role.
Thus, when parasitized in the intestines of individuals, the disease may be asymptomatic (except in cases of infection by very large parasites). Characteristic signs of the chronic phase of intestinal helminthiasis are dyspeptic disorders. In children, asthenoneurotic and pain syndrome are more pronounced. With a massive invasion of roundworms, the development of intestinal obstruction, obstructive jaundice, and pancreatitis is possible.
In people who suffer from helminthiases, due to a weakened immune system and an intensified process of cell division (a consequence of the constant renewal of tissues damaged by parasites), the risk of malignant tumors increases significantly.
Types of helminths that parasitize in the human body
The causes of human helminthiasis are 2 types of worms: roundworms (nematodes) and flatworms (tapeworms).
Roundworms
Pinworm
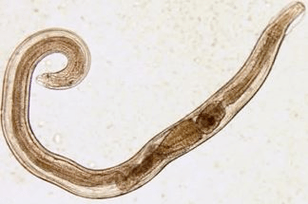
The parasites that cause enterobiasis are small (up to 10 mm) thin worms of the cavity of gray-white color. Infection occurs through food (through the mouth). The reason for that is dirty hands. Parasite eggs can be found in the ground, on the wool of infected animals, unwashed vegetables and fruits, etc. At the same time, in enterobiasis, there are frequent cases of self-infection (especially in children), which are the result of scratching the itchy area and subsequent swallowing of eggs. The pinworm larva develops in the digestive tract within two weeks. Turning into an adult, the worm parasitizes in the lower parts of the small and upper part of the large intestine.
Ascaris
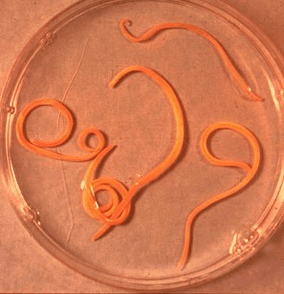
Ascaris is a large red-yellow spindle parasite that reaches 40 cm (females) and 15-25 cm (males) in adulthood. Without dinghies or other fastening devices, the roundworm can move independently towards food masses. Eggs laid by a female parasite are excreted along with the feces.
Vlasoglav
Vlasoglav, the cause of trichocephaly, is a white helminth that parasitizes on the initial part of the colon and reaches a size of 4-5 cm. The parasite feeds on blood and tissues of the rectal mucosa.
With a small number of worms, trichocephaly is asymptomatic. In the severe phase (with massive invasion), the patient develops abdominal pain, severe diarrhea develops, sometimes accompanied by rectal prolapse. This condition is most commonly seen in debilitated children. With a moderate phase of trichocephaly, a developmental delay in the child is possible.
Trichinella

The cause of trichinosis is a small round helminth, which reaches a length of 2-5 mm. Infection occurs when eating poorly roasted meat (pork, bear meat, wild boar). Penetrating into the intestines, the larva of the parasite matures in 3-4 days to the state of a sexually mature individual. The lifespan of the worm is 40 days, after which the parasite dies. By piercing the intestinal wall, the larvae enter the bloodstream and are transmitted to all organs of the human body, settling in the muscles. In this case, the respiratory and facial muscles are most often affected, as well as the flexor muscles of the limbs.
In the first days after the invasion, patients complain of abdominal pain. Then, after about 2 weeks, the body temperature rises to 39-40 C, itchy rashes appear on the skin, muscle pain develops and the face swells. During this period, in the case of a mass infection, there is a significant risk of death. After about a month, the patient recovers. The parasite encapsulates in a spiral shape, after which it dies within two years.
Hookworm and some
These two parasites are similar in biological characteristics as well as in the diseases caused. In this regard, it is common to combine them under a common name (ankylosing). Worms, which reach a length of 10-15 mm, parasitize in 12 p. intestines. It should be noted that this is one of the most common, but at the same time very rarely detected parasites. Worm larvae enter the human body through the skin after contact with contaminated soil. Further, entering the bloodstream, they migrate like worms into the lungs and then, through the bronchi, together with the expectorant sputum, into the digestive tract. Hookworm parasitizes in the intestines, attaching to the intestinal wall. Therefore, the most characteristic symptom of this helminthiasis is anemia due to iron deficiency, as well as changes in the ratio of protein fractions (dysproteinemia).
Flatworms
Wide ribbon
This is one of the largest helminths, reaching a length of 10-20 meters. The disease caused by this parasite is called diphyllobotriasis. The worm development cycle begins with freshwater fish or crabs. The larva enters the human body, which is the ultimate owner of the broad tapeworm, along with eggs or infected fish fillets. Reaching the small intestine, the parasite attaches to its wall and grows in a mature individual within 20-25 days.
Diphyllobotriasis occurs in the background of disorders of the digestive tract and anemia with B12 deficiency.
Hepatic fluke
The parasite that causes opisthorchiasis is a flatworm that reaches a length of 7-20 mm. Human infection occurs when contaminated fish meat that has not undergone sufficient heat treatment is eaten. The larva of the liver fluke from the small intestine penetrates the bile ducts and the gallbladder, fixing itself there with the help of two vacuum cups.
In the acute phase of helminthiasis, the patient has pain in the upper abdomen, body temperature rises, nausea develops, muscle pain is possible, diarrhea and skin rash. The chronic course of opisthorchiasis is manifested by symptoms of hepatitis, inflammation of the bile ducts, cholecystitis, disorders of the digestive tract, nervous disorders, weakness and increased fatigue. The parasite leads to the development of irreversible changes, and even after expulsion the patient does not go through chronic inflammatory processes and functional disorders.
Beef and pork tapeworm
These parasites, almost identical in structure, reach a length of 5-6 meters. Infection with teniarinhoza and teniaza occurs due to the consumption of beef or pork infected with Finns (one of the middle forms of helminthiasis). Sustainable Finns, presented in the form of whitish bubbles that reach a size of 0, 5 cm, attach to the wall of the small intestine of man and in 3 months turn into an adult. The tapeworm parasite, which consists of more than 2, 000 segments, is constantly growing.
Echinococcus
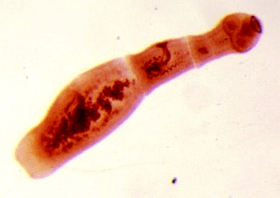
For this parasite, the person is the middle host. The worm parasitizes on the human body in the form of Finns. The final owner of an echinococcus is a wolf, a dog or a cat. The infection occurs through food through contact with animals and objects from the environment with Echinococcus eggs. After entering the intestine, oncospheres (larvae with six hips) develop from them. They enter the bloodstream from the intestines and are transmitted throughout the body.
Alveococcus
This parasite, which is considered a type of echinococcus, is the cause of one of the most dangerous helminthiasis (alveococcosis), which is similar in severity to cirrhosis and liver cancer. Infection occurs when oncospheres (eggs with mature larvae) penetrate the intestines. Laurocysts are very aggressive formations that are constantly growing due to the enlargement of the vesicles, and also have the ability to grow into the liver, like cancer metastases. Necrotic changes due to vascular dysfunction undergo necrotic changes in nearby tissues. Spreading to nearby structures, the alveococcus forms fibrous nodules with inclusions of multidirectional bubbles. This condition can last for several years and therefore requires mandatory surgical intervention.
Diagnosis of helminthiasis
Diagnosis of helminthic invasions includes the following activities:
- careful collection of medical history to help identify possible causes of infection;
- laboratory tests of feces, blood, intestinal contents 12p, rectal and perianal mucus, muscle tissue, lung sputum, bile. Analysis can detect eggs, segments or fragments of the parasite. At the same time, the increased content of eosinophils in the blood is also a signal of the presence of helminthiasis.
- when diseases caused by larval stages or tissue parasites are diagnosed, serological tests (ELISA, RSK, indirect agglutination reaction, immunofluorescence analysis, etc. ) are performed.
- to identify worms affecting liver tissue, ultrasound, CT, and endoscopic studies were prescribed.
Worms in humans: treatment
In the acute phase of parasitic infection, the patient is prescribed detoxification and desensitization therapy. In severe cases of the disease (liver trematodes, trichinosis), glucocorticoids are used according to medical indications.
Special anthelmintic chemotherapeutic agents are prescribed as drugs for specific therapy, taking into account the nature of the pathogen.
At the same time, the patient is recommended to take antihistamines and enterosorbents. The last phase of treatment involves the use of probiotics that normalize the intestinal microflora.
A special gentle diet is also prescribed (food should be digestible and low in fat).
During the period of anthelmintic therapy, the patient must strictly observe personal hygiene (in order to avoid re-infection). At the same time, for many helminthiasis, all family members and people who are in constant contact with the infected must undergo treatment.
Underestimating their danger, combined with a lack of awareness of the biology of these creatures and ways of infecting them, has led to the fact that at least a few billion people today are carriers of certain parasites.
Parasites can be present not only in humans but even outside the human body.
Prevention of parasite infestation
Rule # 1:you can’t eat anything from fish that isn’t salted, fried, or cooked enough. Sushi, lightly salted herring or sashimi can be considered gourmet food. But it is basically a raw fish, and fish is one of the components of the life cycle of parasitic worms.
How it all happens:first the larva enters the mollusk, where it grows no more than a certain limit, then the fish eats the mollusk, the larva enters its digestive tract, remaining alive, then it grows and multiplies, entering the muscle tissue of the fish, then this fish is eaten by dolphin, seagull or polarbear. Or a restaurant visitor who chooses to join high Japanese culture.
Safe raw fish exists in theory. To do this, it must either be frozen immediately after catch and thawed just before cooking, or it must be specially farmed on a fish farm with the control of the absence of parasites. But it is usually impossible to check whether a risky dish has really been prepared from it.
The same must be taken care of with meat; don’t try raw minced meat and fresh salted bacon.
In addition, in order not to get infected with helminths, vegetables must be washed before eating, as well as hands. These parasites have been found to be widespread almost everywhere in the human body as an integral part of the natural environment.
Any contact of food or hands with the ground, dirt and vegetation can leave their microscopic eggs on the food. If they enter the intestines, worms will hatch from the eggs, which will not be easy to remove.
There are parasites that attack a person walking or relaxing in nature, for example:
- Plasmodium malaria, contained in the saliva of mosquitoes of the genus Anopheles,
- the causative agent of encephalitis contained in the saliva of ixodic ticks,
- gadfly and wolfarth fly.
Their prevention consists in the use of all types of repellents in hiking in the wild, as well as in the maximum protection of open areas of the body (mosquito nets, nets, special gel).
However, what can you do if prevention has not helped? Since the attack has been known for a long time, treatment by folk methods has been known for a long time.
And in conclusion, it can be noted that compliance with simple hygiene and sanitary rules, the extermination of flies and cockroaches can significantly reduce the risk of parasite infestation, leading to serious consequences.